Describe Two Major Functions of Dna Polymerases
The process of DNA. DNA polymerases bond the nucleotides together to form new strands that are complementary to each template strand.
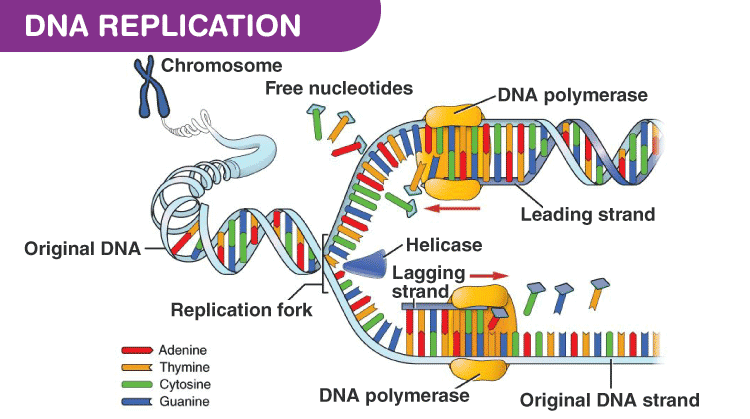
Dna Polymerase Structure Types And Functions
Both types of DNA polymerases possess 5 to 3 polymerizing activity.

. Transcription converts a DNA message into an intermediate molecule called RNA red arrow. The synthesis of DNA during genome replication and the re-synthesis of missing DNA following damage of recombination and following primer excision from the lagging strand. DNA Pols are central players in DNA repair and replicationthe processes that duplicate genomes and maintain their integrity to ensure faithful transmission of genetic information from one generation to other.
It adds nucleotides to the 3 end of the growing chain. Polymerases for DNA repair Several polymerases exist in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Up to 24 cash back process proceeds in two directions at the same time.
Polymerase α-primase Polymerase δ. What are the different DNA polymerases. The function of DNA polymerase is to replicate proofread and repair DNA.
Either a single polypeptide or many polypeptides working together make up a protein green arrow. Both the DNA polymerase I and III have 5 to 3 polymerase activity and 3 to 5 exonuclease activities. In addition both enzymes possess 3 to 5 exonuclease activity for proofreading.
Differences i View the full answer. It detects if there is an error during replication. The DNA Polymerase detects if there is an error it removes the incorrect nucleotide and replaces it with the correct one.
Describe 2 major functions of DNA Polymerases. DNA Polymerases Functions Replication of DNA Polymerases. They perform two primary functions in the cell.
One of the main results was the identification of a novel family of DNA polymerases family Y Ohmori et al 2001 whose members are widely believed to conduct synthesis opposite. The main function of DNA polymerase 3 is its function in the polymerization. It proofreads the nucleotide chain after synthesizing them.
Several DNA polymerases exist but DNA polymerase I or Pol I and DNA polymerase III or Pol III are the main ones involved in DNA replication. They provide polymerase activity under two. The eukaryotic cells consist of major 5 DNA polymerase out of which one is present in the mitochondria and the others are found in the nucleus.
It bonds the new nucleotides together. DNA Pols are central players in DNA repair and replicationthe processes that duplicate genomes and maintain their integrity to ensure faithful transmission of genetic. It adds nucleotides to the DNA and proofreads the created portion of DNA.
It bonds the new nucleotides together. 2 Free-floating nucleotides pair one by one with the bases on the template strands as they are exposed. DNA polymerase enzyme starts its function during replication of DNA at the step of arranging the relevant nucleotides to form hydrogen bonds between corresponding nitrogenous bases of the existing and new DNA strands.
While the unique functions of these DNA polymerases are differentiated by their association. It detects if there is an error during replication. The main function of DNA polymerase is to synthesize a new DNA strand.
DNA polymerases are vital for the synthesis of new DNA strands. This chapter focuses on DNA polymerases Pols and their functions. DNA polymerase performs several functions during replication.
The repair process is very important for maintaining integrity in the genomes because the repair is a. DNA polymerase is one of the most important enzymes in DNA replication which is the process whereby new copy of DNA molecule is synthesized. Enzymes catalyzing DNA synthesis on a DNA template are DNA Polymerases.
DNA polymerases are the molecular precursors of DNA deoxyribonucleic acid. Describe two major functions of the DNA polymerases. 15 rows Perhaps the most important function of DNA polymerases is to synthesize an exact replica of.
Apart from this DNA polymerase is also involved in correcting the errors of added nucleotides in a process known as proofreading. DNA polymerase works by sliding along the single strand template of DNA reading its nucleotide bases as it goes along and inserting new complementary nucleotides into the primer so as to make a sequence complementary to the template. The two functions of DNA polymerase are as follows.
It synthesized the DNA. Replication is the main function of DNA polymerases. Proofreading helps to maintain the integrity of the double-stranded DNA.
DNA replication occurs in a smooth continuous way on one of the strands. DNA polymerase is thought to be able to replicate 749 nucleotides per second. Since the discovery of DNA polymerase I in Escherichia coli a diverse library of mammalian DNA polymerases involved in DNA replication DNA repair antibody generation and cell checkpoint signaling has emerged.
They are types of enzymes. Additionally it removes the RNA primer from the DNA. Translation interprets an RNA message into a string of amino acids called a polypeptide.
DNA polymerase 1 and 3 are two types of DNA polymerases involved in prokaryotic DNA replication. Critical for DNA replication are three DNA polymerases. The DNA Polymerase detects if there is an error it removes the incorrect nucleotide and replaces it with the correct one.
What are two functions of DNA polymerases in DNA replication. DNA polymerase I and III both are prokaryotic enzymes. Similarities in enzymatic activities of between DNA polymerase I and III.
This chapter focuses on DNA polymerases Pols and their functions. The four DNA polymerases found in the nucleus are responsible for DNA replication.

1 Dna Replication Is Semi Conservative 2 Dna Polymerase Enzymes Are Specialized For Different Functions 3 Dna Pol I Has 3 Activities Polymerase 3 5 Ppt Download

How Many Types Of Dna Polymerase Are Present In Bacteria
Difference Between Dna And Rna Polymerase Definition Replication Transcription Process
Comments
Post a Comment